Home /
Expert Answers /
Economics /
4-refer-to-the-diagram-for-a-monopolistically-competitive-firm-in-short-run-equilibrium-this-firm-pa534
(Solved): 4. Refer to the diagram for a monopolistically competitive firm in short-run equilibrium. This firm ...
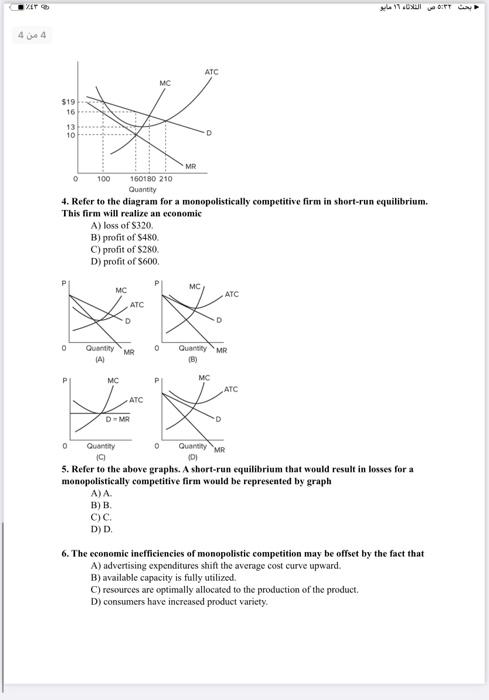


4. Refer to the diagram for a monopolistically competitive firm in short-run equilibrium. This firm will realize an economic A) loss of . B) profit of . C) profit of D) profit of . 5. Refer to the above graphs. A short-run equilibrium that would result in losses for a monopolistically competitive firm would be represented by graph A) A. B) B. C) . D) D. 6. The economic incficiencies of monopolistic competition may be offset by the fact that A) advertising expenditures shift the average cost curve upward. B) available capacity is fully utilized. C) resources are optimally allocated to the production of the product. D) consumers have increased product variety.
5. If the industry depicted in this graph were served by a pure monopoly, the price and output quantity would be A) and 1. B) and . C) and . D) and . 6. To practice long-run price diserimination, a monopolist must A) be a natural monopoly. B) charge one price to all buyers. C) permit the resale of the product by the original buyers. D) be able to separate buyers into different markets with different price elasticities. Chapter 13 1. Which of the following is NOT a basic characteristic of monopolistic competition? A) the use of trademarks and brand names B) recognized mutual interdependence C) product differentiation D) a relatively large number of sellers 2. A significant difference between a monopolistically competitive firm and a purely competitive firm is that the A) former has fewer barriers to entry into the industry. B) latter recognizes that price must be reduced to sell more output. C) latter's demand curve is perfectly elastic. D) latter differentiates its product. 3. In the long run, a representative firm in a monopolistically competitive industry will end up A) having an elasticity of demand that will be less than it was in the short run. B) having a larger number of competitors than it will in the short run. C) producing a level of output at which marginal cost and price are equal. D) earning a normal profit, but not an economic profit.
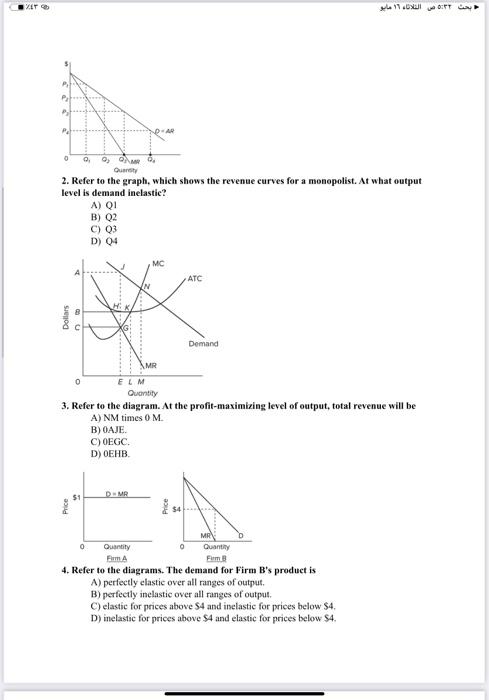
2. Refer to the graph, which shows the revenue curves for a monopolist. At what output level is demand inelastie? A) B) C) D) 3. Refer to the diagram. At the profit-maximbing level of output, total revenue will be- A) NM times B) . C) . D) 0EHB. 4. Refer to the diagrams. The demand for Firm B's produet is A) perfectly elastic over all ranges of output. B) perfectly inelastic over all ranges of output. C) elastic for prices above and inelastic for prices below . D) inelastic for prices above and elastic for prices below .
ECON101-Term 222 -Chapters Handout Chapter 12 Problem Questions Question 1 Suppose a monopoly is facing the following equations: Market demand, Total cost function, . Marginal Cost, Marginal Revenuc, a. How much profitloss does the monopoly ear? Show all your work. b. Graph all your findings and calculate the deadweight loss (DWL) under the monopoly. c. Find the income transfer level from consumer to monopoly. d. Suppose the monopolist's fixed costs change to . Find the new profit of the monopoly. What does this tell you about the costs of obtaining a monopoly? Question 2 A new production technology for making vitamins is invented by a college professor who decides not to patent it. Thus, it is available for anybody to copy and put into use. The TC per botle for production up to 100,000 bottles per day is given in the following table. a. What is ATC for each level of output listed in the table? b. Suppose that for each 25,000 -bottle-per-day inerease in production above 100,000 bottles per day, TC increases by (so that, for instance, 125,000 bottles per day would generate total costs of and 150,000 botles per day would generate total costs of . Is this a decreasing cost industry? c. Suppose that the price of a bottle of vitamins is and that at that price the total quantity demanded by consumers is bottles. How many firms will there be in this industry? d. Suppose that, instead, the market quantity demanded at a price of is only 75,000 . How many firms do you expect there to be in this industry? e. Review your answers to parts , , and d. Does the level of demand determine this industry's market structure? f. Compare your answer to part d of this problem with your answer to part d of problem 3. Do both production technologies show constant returs to scale? 1. With respeet to the pure monopolist's demand curve, it can be said that A) the stronger the barriers to entry, the more elastic is the monopolist's demand curve. B) price exceeds marginal revenue at all outputs greater than 1 . C) demand is perfectly inclastic. D) marginal revenue equals price at all outputs.
Expert Answer
A monopolistically competitive market is characterized by firms that se...