Home /
Expert Answers /
Electrical Engineering /
a-ferromagnetic-material-as-shown-with-a-square-cross-sectional-area-of-16cm2-has-a-relative-permea-pa364
(Solved): A ferromagnetic material as shown with a square cross-sectional area of 16cm2 has a relative permea ...
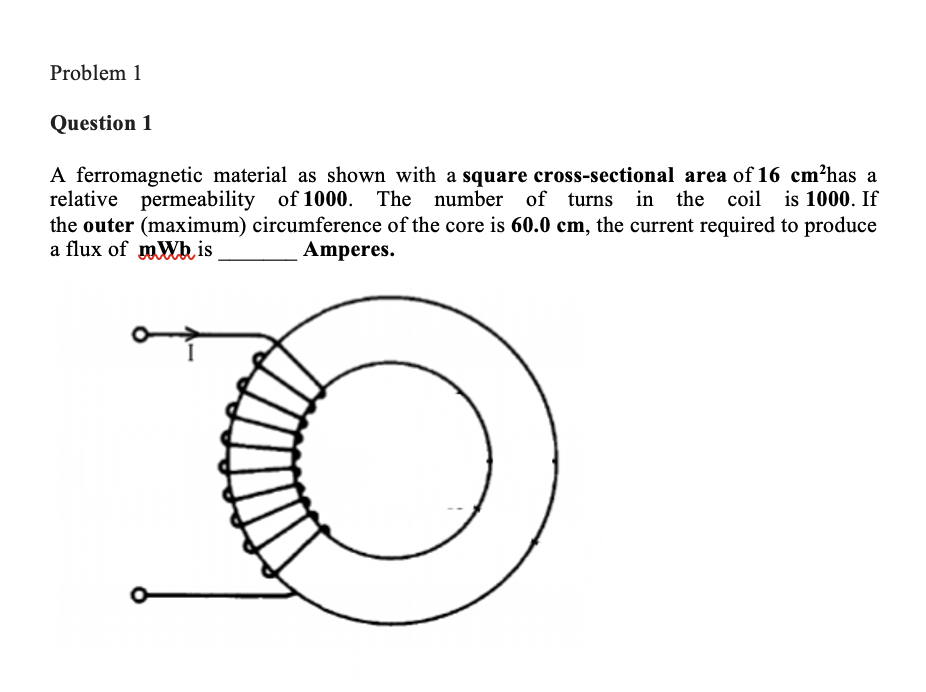
A ferromagnetic material as shown with a square cross-sectional area of has a relative permeability of . The number of turns in the coil is . If the outer (maximum) circumference of the core is , the current required to produce a flux of is Amperes.
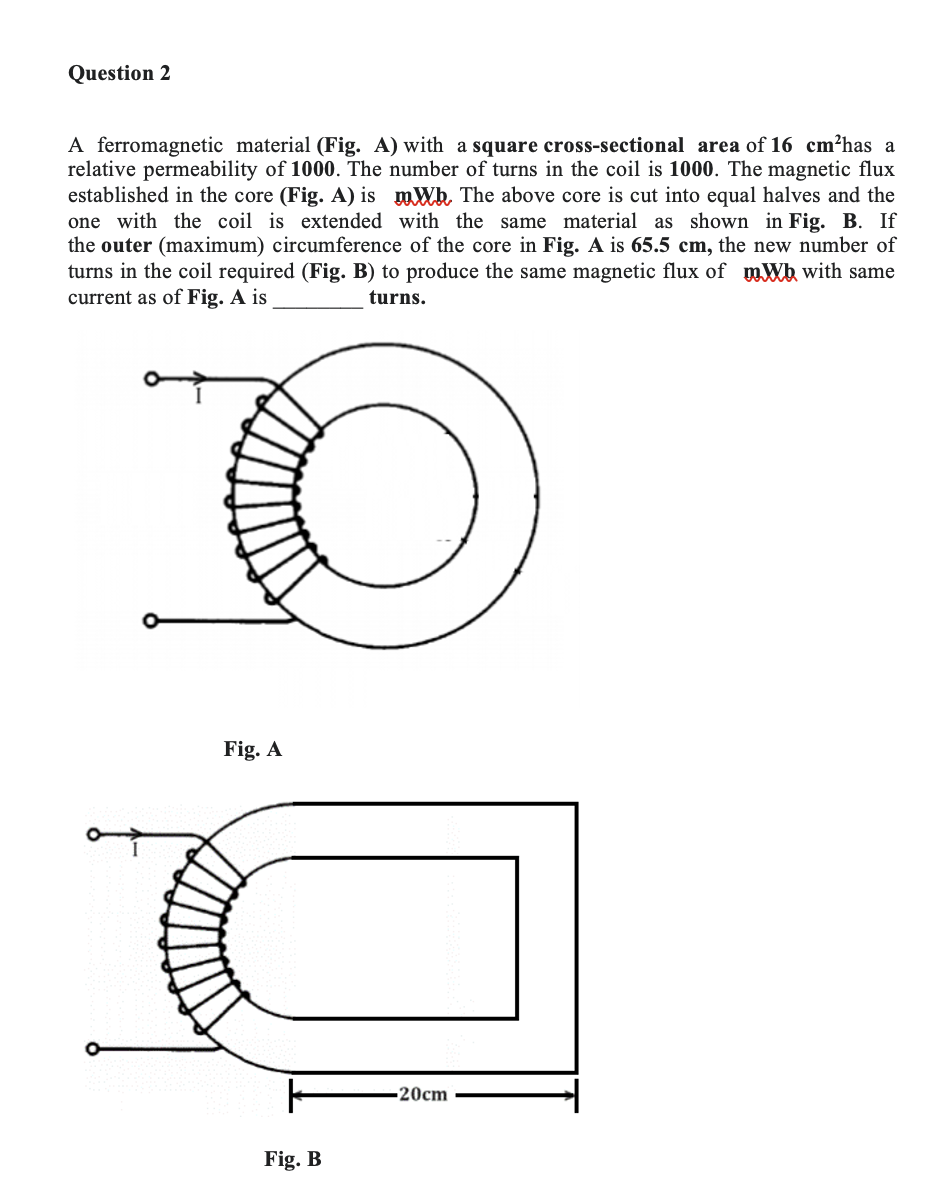
A ferromagnetic material (Fig. A) with a square cross-sectional area of has a relative permeability of . The number of turns in the coil is . The magnetic flux established in the core (Fig. A) is . The above core is cut into equal halves and the one with the coil is extended with the same material as shown in Fig. B. If the outer (maximum) circumference of the core in Fig. A is , the new number of turns in the coil required (Fig. B) to produce the same magnetic flux of with same current as of Fig. is turns. Fig. A
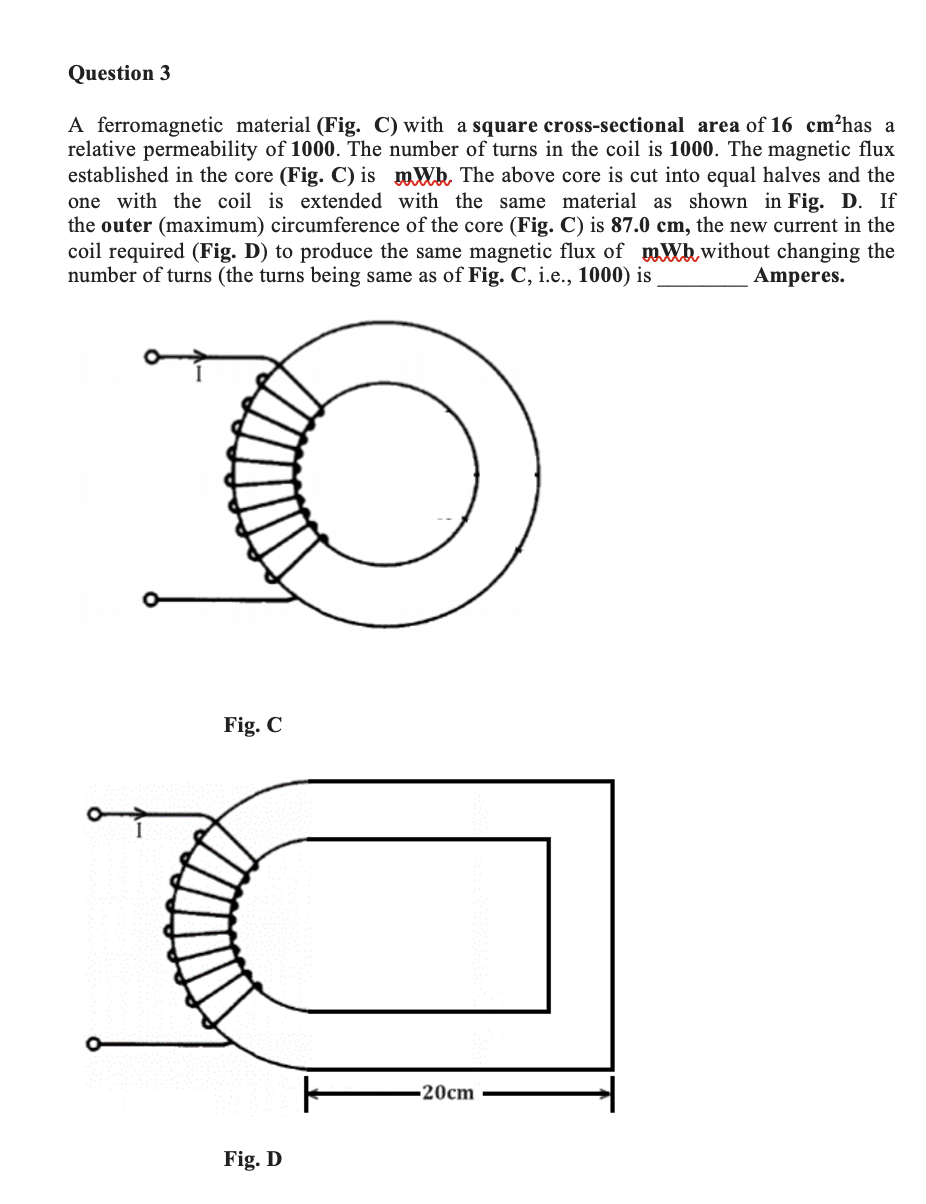
A ferromagnetic material (Fig. C) with a square cross-sectional area of has a relative permeability of . The number of turns in the coil is . The magnetic flux established in the core (Fig. C) is . The above core is cut into equal halves and the one with the coil is extended with the same material as shown in Fig. D. If the outer (maximum) circumference of the core (Fig. C) is , the new current in the coil required (Fig. D) to produce the same magnetic flux of without changing the number of turns (the turns being same as of Fig. C, i.e., 1000) is Amperes. Fig. C Fig. D