Home /
Expert Answers /
Geometry /
a-standard-proof-of-the-pythagorean-theorem-starts-with-a-right-triangle-abc-with-its-right-angles-pa610
(Solved): A standard proof of the Pythagorean theorem starts with a right triangle ABC, with its right angles ...
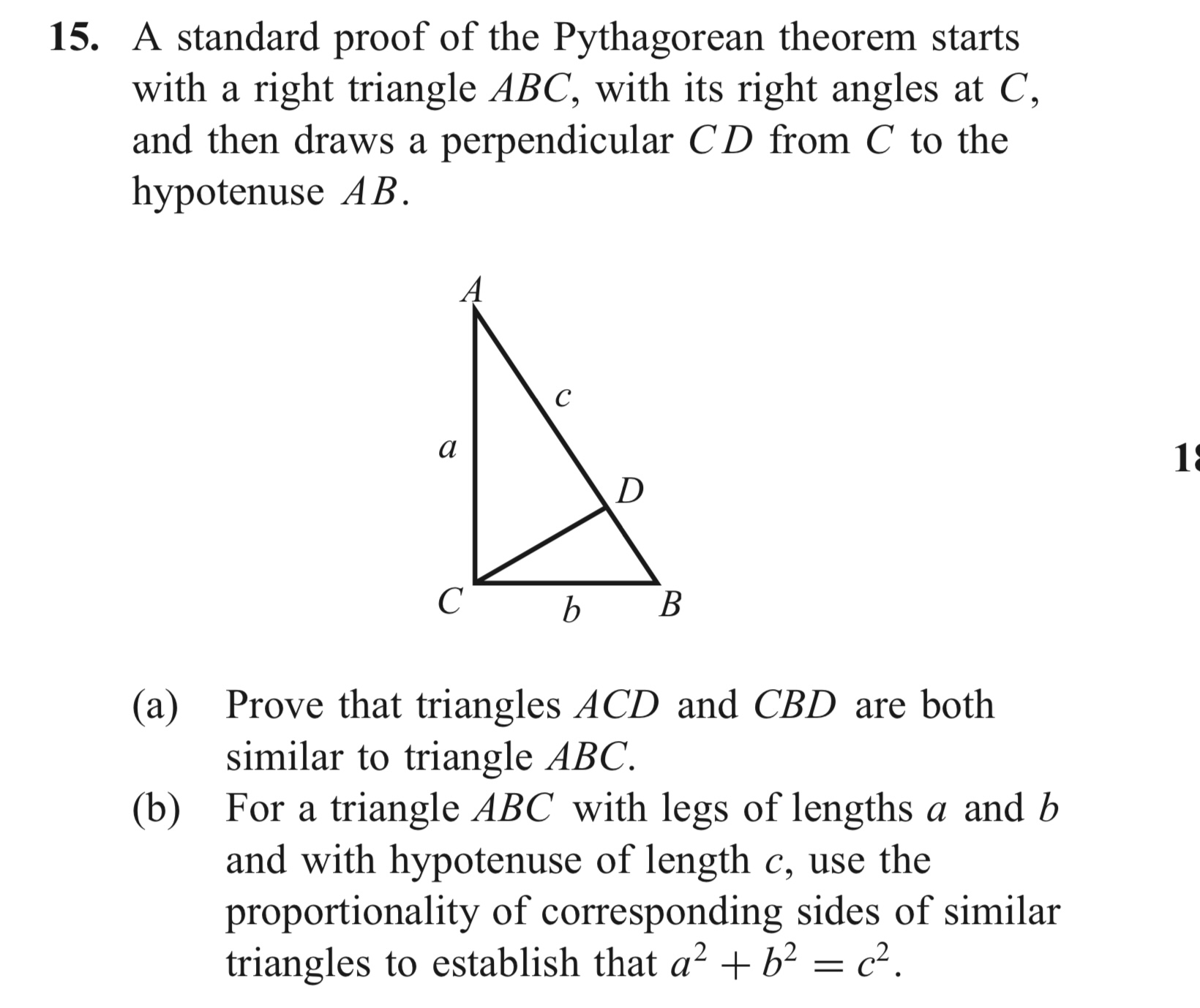
A standard proof of the Pythagorean theorem starts
with a right triangle ABC, with its right angles at C,
and then draws a perpendicular CD from C to the
hypotenuse AB.
(a) Prove that triangles ACD and CBD are both
similar to triangle ABC.
(b) For a triangle ABC with legs of lengths a and b
and with hypotenuse of length c, use the
proportionality of corresponding sides of similar
triangles to establish that a^(2)+b^(2)=c^(2).