Home /
Expert Answers /
Anatomy and Physiology /
anybody-who-has-knowledge-about-the-histology-of-intestinal-glands-and-villi-help-me-with-this-ques-pa522
(Solved): anybody who has knowledge about the histology of intestinal glands and villi, help me with this ques ...
anybody who has knowledge about the histology of intestinal glands and villi, help me with this question?
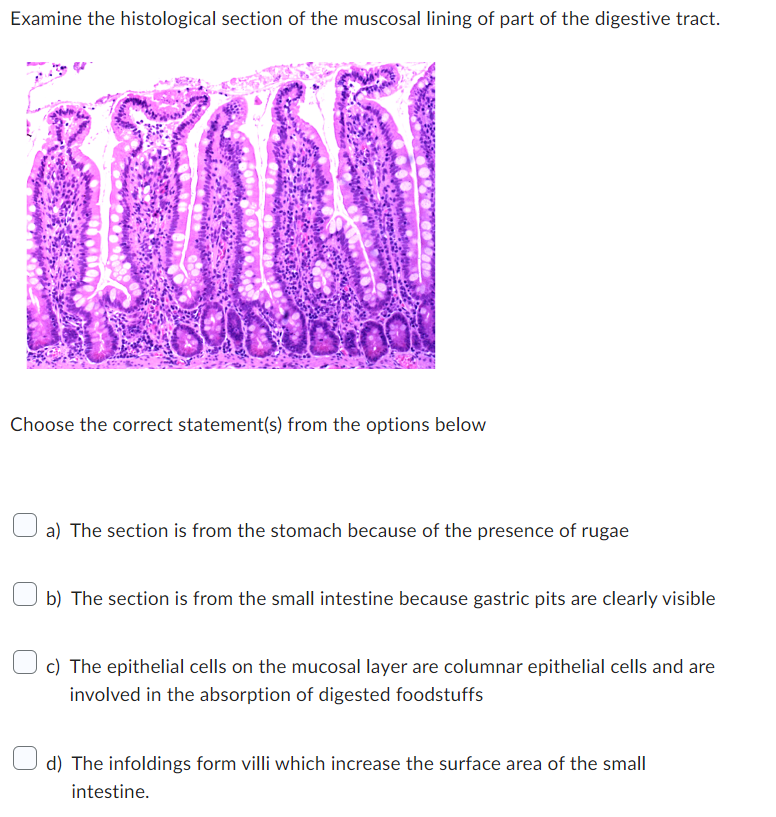
Examine the histological section of the muscosal lining of part of the digestive tract. Choose the correct statement(s) from the options below a) The section is from the stomach because of the presence of rugae b) The section is from the small intestine because gastric pits are clearly visible c) The epithelial cells on the mucosal layer are columnar epithelial cells and are involved in the absorption of digested foodstuffs d) The infoldings form villi which increase the surface area of the small intestine.
Expert Answer
A histological section of the mucosal lining of the digestive tract would reveal the various layers and structures that make up the lining of the digestive system.The different layers are typically seen in a histological section:1. Mucosa: The mucosa is the innermost layer of the digestive tract. It consists of three sub-layers: a. Epithelium: This layer is in direct contact with the contents of the digestive tract. The type of epithelium can vary depending on the location in the digestive system. For example, simple columnar epithelium with microvilli is commonly found in the small intestine, while stratified squamous epithelium is found in the esophagus. b. Lamina propria: This layer is the connective tissue that supports the epithelium. It contains blood vessels, lymphatics, and immune cells. c. Muscularis mucosae: This thin layer of smooth muscle helps with the movement and folding of the mucosa.2. Submucosa: The submucosa is a layer of connective tissue located beneath the mucosa. It contains blood vessels, lymphatics, and nerves that supply the mucosa. It also contains submucosal glands in some areas.3. Muscularis externa: This layer consists of smooth muscle responsible for the movement and peristalsis of the digestive tract. It is typically divided into an inner circular layer and an outer longitudinal layer of muscle fibers.4. Adventitia or Serosa: Depending on the location, the outermost layer of the digestive tract can be either adventitia or serosa. The adventitia is composed of connective tissue that attaches the digestive tract to surrounding structures, while the serosa is a smooth, thin layer of connective tissue covered by a mesothelium. The serosa is found in the abdominal portion of the digestive tract.