Home /
Expert Answers /
Advanced Physics /
comparing-the-transistorized-voltmeter-with-an-ordinary-voltmeter-from-the-observations-already-gi-pa836
(Solved): Comparing the transistorized voltmeter with an ordinary voltmeter. From the observations already gi ...
Comparing the transistorized voltmeter with an ordinary voltmeter.
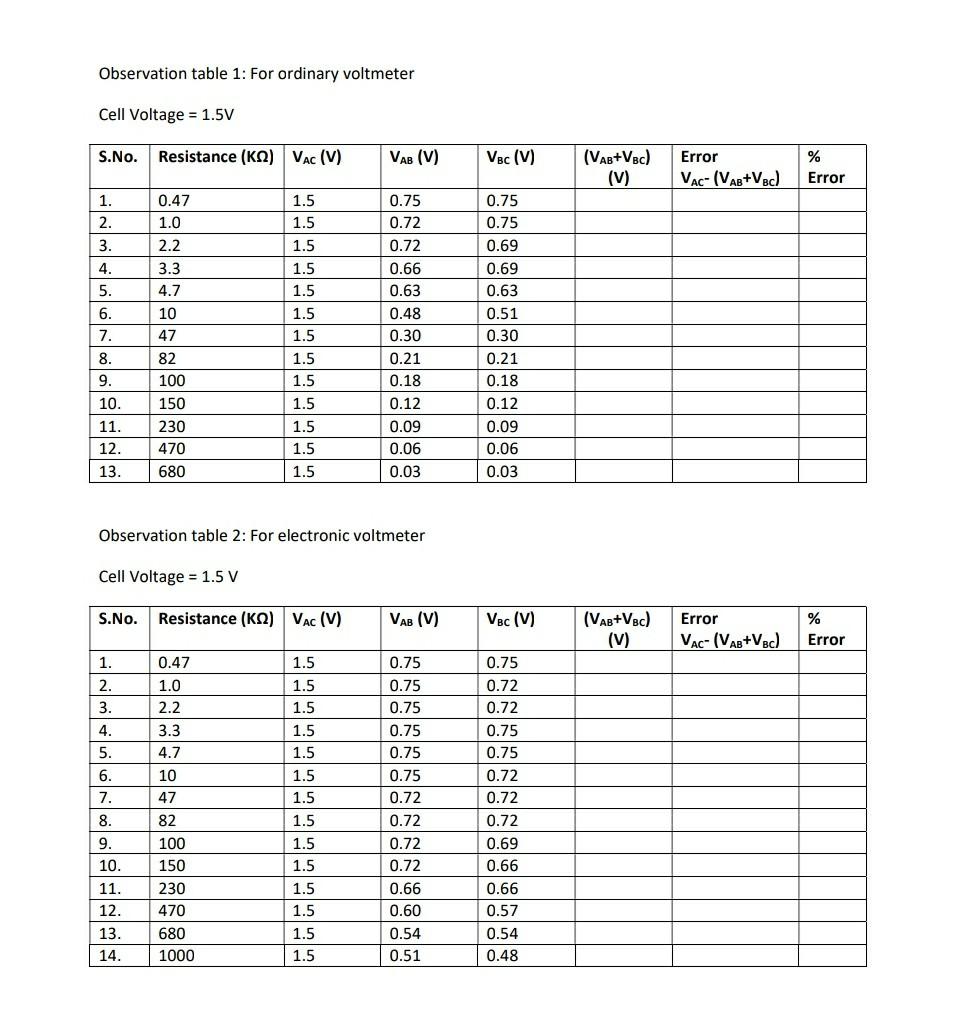
From the observations already given do the calculations and fill the other quantities in the table.
Draw graph on graph paper between percentage error vs R for both transistorized voltmeter and ordinary voltmeter. Do the calculations using the graphs.
Also provide the precautions to be followed in this experiment.
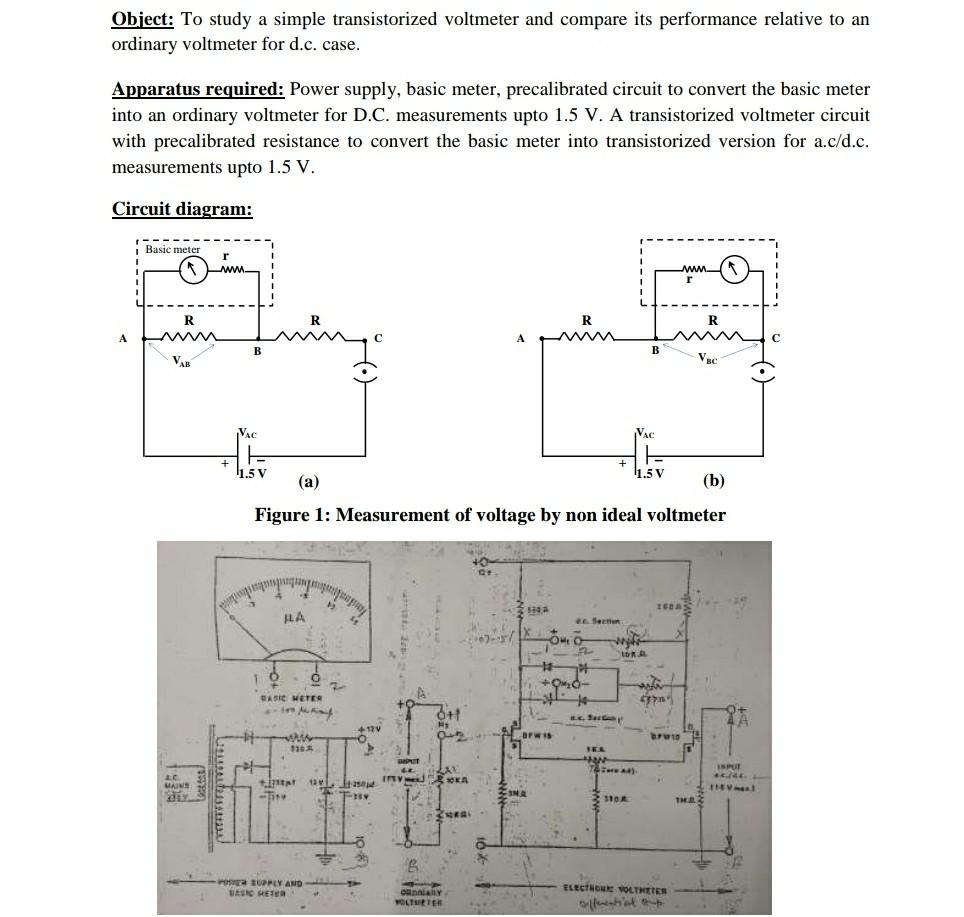


Object: To study a simple transistorized voltmeter and compare its performance relative to an ordinary voltmeter for d.c. case. Apparatus required: Power supply, basic meter, precalibrated circuit to convert the basic meter into an ordinary voltmeter for D.C. measurements upto 1.5 V. A transistorized voltmeter circuit with precalibrated resistance to convert the basic meter into transistorized version for a.c/d.c. measurements upto 1.5 V. Circuit diagram: A Basic meter R VAB &.C. MAINE Faz r www B VAC 1.5 V 1 HLA R BASIC METER + <-Tite 100 Maf sass 1105 POSER SUPPLY AND BASIC HETER 12 121, I M65 (a) Figure 1: Measurement of voltage by non ideal voltmeter +12V FI IMPUT ITTY MEL. 6+1 H? AV KOKA -EuRai B oannially VOLTHETER A 114 A IMA R ww ONE # BFWIS c. Section Z -94?0- * L.C. Serdany IKA HAN IDR.A Tere Ad) B VAC 110M 1.5 V www. r 160A este (370² BFWID ELECTRONIC VOLTHETER offerential p R V? THE 2 BC (b) ISPUT acide. C IMVmant 2 ?
Theory and Formula used: For internal resistance: In figure 1, the current (I) will be same as the resistance "R" is in series and is given by equation (1). If in figure 1, when a voltmeter of internal resistance r (shown as dashed box) is connected across any resistance R, the measured value is decreased due to parallel combination of R & r. & VAB = VBC (1) VAB VBC R I= = R When the voltmeter of internal resistance r is connected across any resistance "R" then total current across the circuit is given by: I= V total VAC = VAC Rtotal R+R||r (R+r) R (R+2r) If voltmeter of internal resistance r is connected in parallel with R then VAB is given by: rR R+r Substitute value of I from equation (2) in equation (3) VABI X VAB = VAC = Error = (R+r) R (R+2r) rR XR+r If we solve it further Now error can be calculated using Error = VAC - (VAB + VBC) = VAC-(2VAC (R+2r) € - €0= (R+r) R (R+r)+ rR (R+r) = VAC R² + 2TR (R+T) TR = VACK (R+2r) R+ VAC R+2r = VAC(R+2r)-2rVAC VAC R +2rVAC-2rV AC R+2r R+2r Thus, Error = VAC- (VAB + VBC) = VA AC R R+2r R R+2r If we simplify above equation we get x 100 ? A= R R+2r x 100 = VAC = VAC R R+2r x 100 = R R+2r x 100; For R = 0, € = 0. VAC- (VAB+ VBC) Theoretically, percentage error (€) = VAC However, experimentally we find that € = €, (using graph) for R = 0. So the above formula is modified as: (2) (3) (VAB VBC (from eqn. 1)} (For simplicity we take (e-E, A))
A (R+ 2r) =R x 100 or, 2rAR (100 - A) R (100- A) 2 ? • r = A = € - Eo ? % error observed for the resistance R and to is its value when the graph is extrapolated to include R = 0.
Observation table 1: For ordinary voltmeter Cell Voltage = 1.5V S.No. Resistance (K) VAC (V) 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 1. 2. 3. EEEEECONOSAU 4. 5. 0.47 1.0 ONM 7. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 2.2 3.3 4.7 10 47 82 100 150 230 470 680 1.5 1.5 1.5 1.5 1.5 0.47 1.0 2.2 3.3 4.7 10 47 82 Cell Voltage = 1.5 V S.No. Resistance (K) VAC (V) 100 150 230 470 680 1000 1.5 555L 1.5 Observation table 2: For electronic voltmeter 1.5 1.5 1.5 1.5 ini 1.5 1.5 ?? ?? ?? ?? ?? ?? ?? ?? ?? ?? ?? ?? ?? ?? 1.5 in 1.5 ininininin 1.5 1.5 1.5 1.5 1.5 in in in 1.5 1.5 1.5 i5555 1.5 1.5 1.5 VAB (V) 1.5 0.75 0.72 0.72 0.66 0.63 0.48 0.30 0.21 0.18 0.12 0.09 0.06 0.03 VAB (V) 0.75 0.75 0.75 0.75 0.75 0.75 0.72 0.72 0.72 0.72 0.66 0.60 0.54 0.51 Vac (V) 0.75 0.75 0.69 0.69 0.63 0.51 0.30 0.21 0.18 0.12 0.09 0.06 0.03 Vsc (V) 0.75 0.72 0.72 0.75 0.75 0.72 0.72 0.72 0.69 0.66 0.66 0.57 0.54 0.48 (VAB+VBC) (V) (VAB+VBC) (V) Error VAC- (VAB+VBC) Error VAC- (VAB+VBC) % Error % Error