(Solved): J. J. Thomson is best known for his discoveries about the nature of cathode rays. His other importan ...
J. J. Thomson is best known for his discoveries about the nature of cathode rays. His other important contribution was the invention, together with one of his students, of the mass spectrometer, a device that measures the ratio of mass
mto (positive) charge
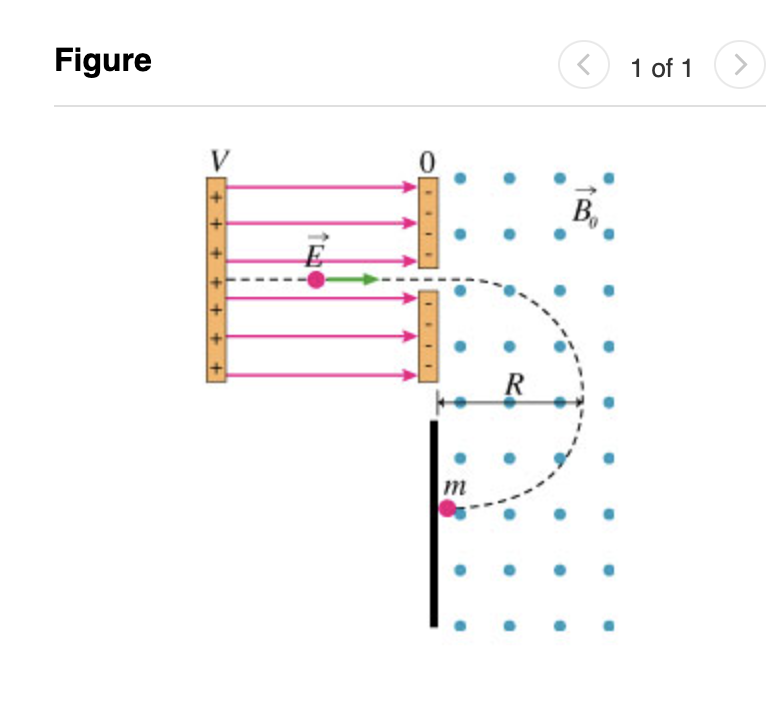
qof an ion. The spectrometer consists of two regions as shown in the figure.(Figure 1) In the first region an electric field accelerates the ion and in the second the ion follows a circular arc in a magnetic field. The radius of curvature of the arc can be measured and then the
(m)/(q)ratio can be found. Part A After being accelerated to a speed of
1.73\times 10^(5)(m)/(s), the particle enters a uniform magnetic field of strength 1.00 T and travels in a circle of radius 33.0 cm (determined by observing where it hits the screen as shown in the figure). The results of this experiment allow one to find
(m)/(q). Find the ratio
(m)/(q)for this particle. Express your answer numerically in kilograms per coulomb. View Available Hint(s)
(m)/(q)=
k(g)/(C)Figure