Home /
Expert Answers /
Physics /
learning-goal-to-apply-the-principle-of-work-and-energy-to-a-rigid-body-the-principle-of-work-and-pa913
(Solved): Learning Goal: To apply the principle of work and energy to a rigid body. The principle of work and ...
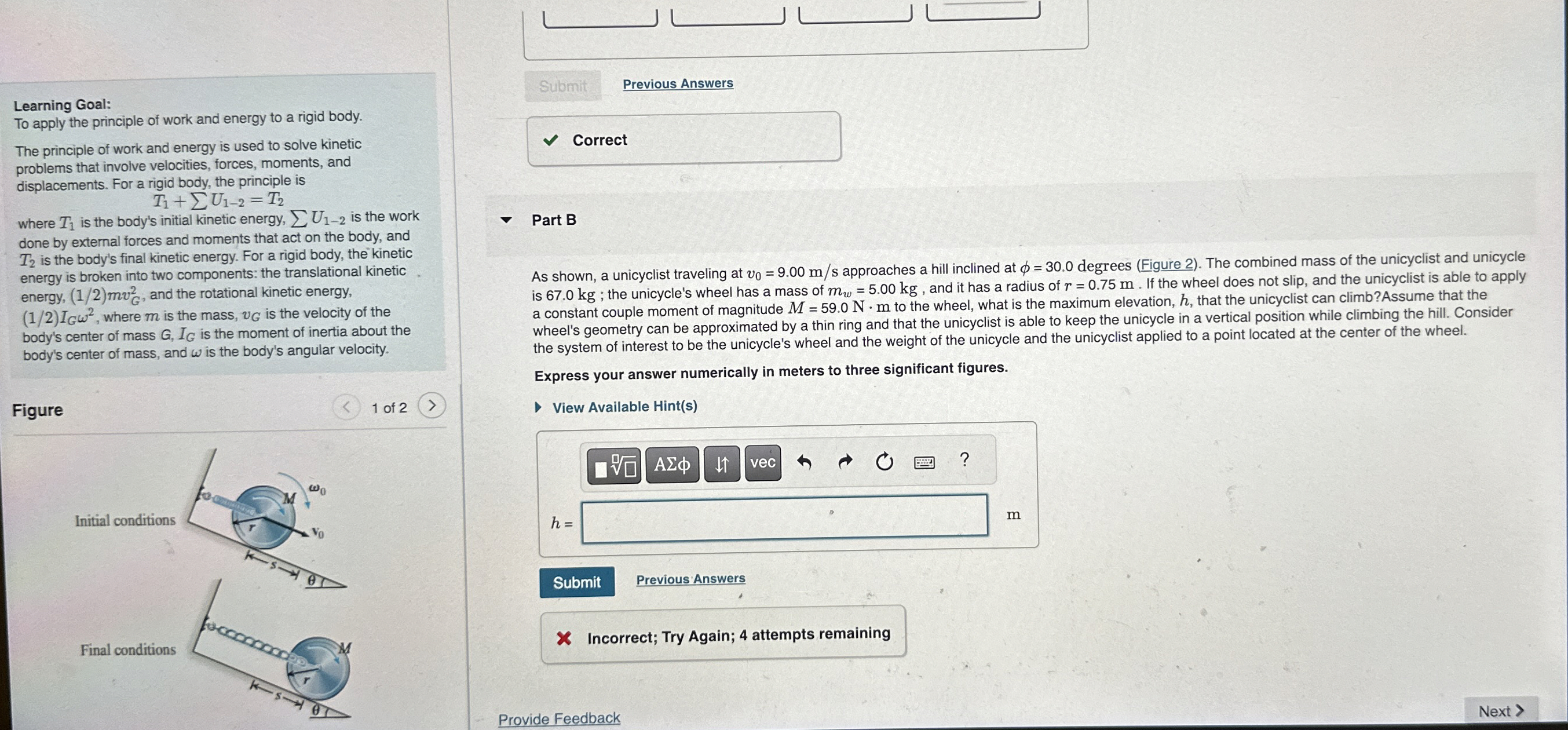
Learning Goal: To apply the principle of work and energy to a rigid body. The principle of work and energy is used to solve kinetic problems that involve velocities, forces, moments, and displacements. For a rigid body, the principle is
T_(1)+\sum U_(1-2)=T_(2)where
T_(1)is the body's initial kinetic energy,
\sum U_(1-2)is the work done by external forces and moments that act on the body, and
T_(2)is the body's final kinetic energy. For a rigid body, the kinetic energy is broken into two components: the translational kinetic energy,
((1)/(2))mv_(G)^(2), and the rotational kinetic energy,
((1)/(2))I_(G)\omega ^(2), where
mis the mass,
v_(G)is the velocity of the body's center of mass
G,I_(G)is the moment of inertia about the body's center of mass, and
\omega is the body's angular velocity. Show work please.