Home /
Expert Answers /
Biology /
nbsp-i-have-some-confusion-from-the-tca-cycle-that-i-would-like-some-help-with-so-in-the-step-w-pa647
(Solved): I have some confusion from the TCA cycle that I would like some help with: So, in the step w ...
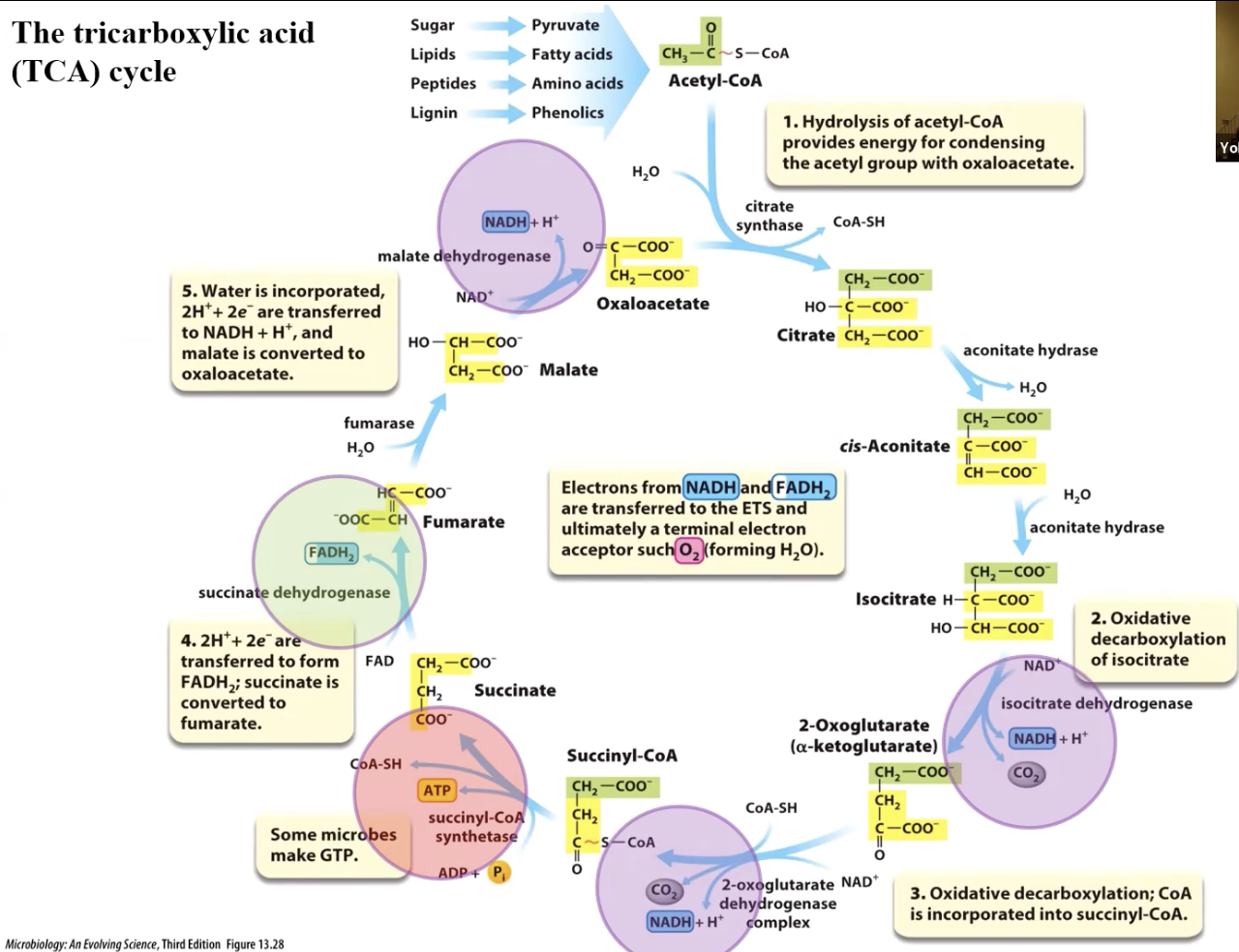
I have some confusion from the TCA cycle that I would like some help with: So, in the step where it goes from isocitrate to alpha-ketogluterate [the right-most purple circle], we observe that NAD+ collects two electrons and an H+ proton. Also, carbon dioxide gets released here. In addition, we see that another H+ proton gets released. My question is how this is possible, as isocitrate has five hydrogen atoms while a-ketogluterate has four hydrogen atoms, while supposedly two hydrogen atoms are being removed from isocitrate. Thanks for the clarification
The tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle 5. Water is incorporated, 2H*+ 2e are transferred to NADH + H*, and malate is converted to oxaloacetate. malate dehydrogenase Microbiology: An Evolving Science, Third Edition Figure 13.28 Sugar Lipids Peptides Lignin fumarase H?O FADH? succinate dehydrogenase HC-COO™ COA-SH Some microbes make GTP. H?—CH—COO NADH+H+ OOC-CH Fumarate NAD* 4.2H+ + 2e are transferred to form FAD CH?-COO™ FADH?; succinate is converted to fumarate. CH?-COO Malate ATP Pyruvate Fatty acids Amino acids Phenolics CH? Succinate COO™ succinyl-CoA synthetase ADP+ P H?O 0 C-COO™ CH?-C S-CoA Acetyl-CoA CH?-COO™ Oxaloacetate Succinyl-CoA CH?-COO CH? C~S-COA 1. Hydrolysis of acetyl-CoA provides energy for condensing the acetyl group with oxaloacetate. citrate synthase CoA-SH Electrons from NADH and FADH? are transferred to the ETS and ultimately a terminal electron acceptor such 0? (forming H?O). H?–C-COO Citrate CH?-COO™ CH?-COO CoA-SH 2-Oxoglutarate (a-ketoglutarate) CO? NADH + H+ complex CH?-COO cis-Aconitate C-COO™ CH-COO aconitate hydrase CH?-COO CH? C-COO 2-oxoglutarate NAD* dehydrogenase H?O CH?-COO Isocitrate H-C-COO™ H?—CH—Coo H?O aconitate hydrase NAD isocitrate dehydrogenase NADH+H+ CO? 2. Oxidative decarboxylation of isocitrate Yol 3. Oxidative decarboxylation; CoA is incorporated into succinyl-CoA.
Expert Answer
Answer: In isocitrate has 8 hydrogen atoms b