Home /
Expert Answers /
Chemistry /
nbsp-nbsp-in-radical-chlorination-of-alkanes-non-equivalent-hydrogens-react-with-chlorine-pa137
(Solved): In radical chlorination of alkanes, non-equivalent hydrogens react with chlorine ...

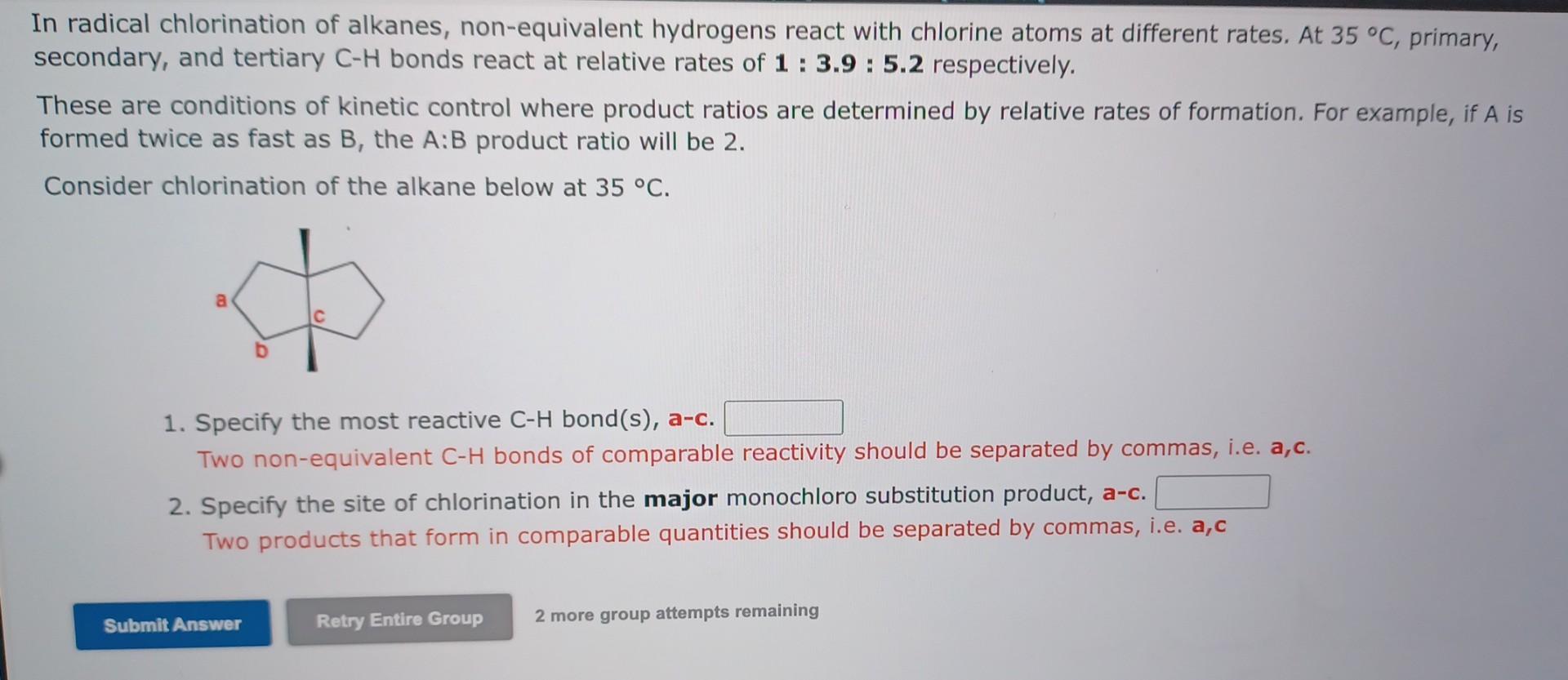
In radical chlorination of alkanes, non-equivalent hydrogens react with chlorine atoms at different rates. At \( 35{ }^{\circ} \mathrm{C} \), primary, secondary, and tertiary \( \mathrm{C}-\mathrm{H} \) bonds react at relative rates of \( 1: \mathbf{3} . \mathbf{2}: \mathbf{5} .2 \) respectively. These are conditions of kinetic control where product ratios are determined by relative rates of formation. For if \( A \) is formed twice as fast as \( B \), the \( A: B \) product ratio will be 2 . Consider chlorination of the alkane below at \( 35^{\circ} \mathrm{C} \). 1. Specify the most reactive C-H bond(s), a-c. Two non-equivalent C-H bonds of comparable reactivity should be separated by commas, i.e. a, c. 2. Specify the site of chlorination in the major monochloro substitution product, a-c. Two products that form in comparable quantities should be separated by commas, i.e. a, c
in radical chlorination of alkanes, non-equivalent hydrogens react with chlorine atoms at different rates. At \( 35^{\circ} \mathrm{C} \), primary, secondary, and tertiary \( \mathrm{C}-\mathrm{H} \) bonds react at relative rates \( 1: \mathbf{3} .9: \mathbf{5} .2 \) respectively. These are conditions of kinetic control where product ratios are determined by relative rates of formation. For example, if \( \mathrm{A} \) is formed twice as fast as \( B \), the \( A: B \) product ratio will be 2 . Consider chlorination of the alkane below at \( 35^{\circ} \mathrm{C} \). 1. Specify the most reactive \( \mathrm{C}-\mathrm{H} \) bond(s), a-c. Two non-equivalent \( \mathrm{C}-\mathrm{H} \) bonds of comparable reactivity should be separated by commas, i.e. a,c. 2. Specify the site of chlorination in the major monochloro substitution product, Two products that form in comparable quantities should be separated by commas, i.e. a,c 2 more group attempts remaining