need help with python homework
 Here is the code I have so far:
Here is the code I have so far:
import math
class GeometricShape:
'''Base/Parent class for all the geometric shapes'''
def __init__(self, name):
'''Constroctor for GeometricShape class'''
self.__name = name
def get_name(self):
'''Returns name of a geometric object'''
return self.__name
def set_name(self, name):
'''Set name of a geometric object'''
self.__name = name
class Rectangle(GeometricShape):
'''Rectangle class which inherits GeometricShape class'''
def __init__(self, length, width, name='Rectangle'):
'''Constructor'''
self.__length = length
self.__width = width
super().__init__(name)
def get_length(self):
'''returns length of a rectangle object'''
return self.__length
def set_length(self, length):
'''set length of a rectangle'''
self.__length = length
def get_width(self):
'''returns width of a rectangle object'''
return self.__width
def set_width(self, width):
'''set width of a rectangle'''
self.__width = width
def get_perimeter(self):
'''Returns perimeter of a rectangle. It is sum of all sides'''
return (2*self.__length) + (2*self.__width)
def get_area(self):
'''Returns area of a rectangle'''
return self.__length * self.__width
class Ellipse(GeometricShape):
'''Ellipse class which inherits GeometricShape class'''
PI = 3.14159 # Constant pi
def __init__(self, semi_major_axis, semi_minor_axis, name='Ellipse'):
'''Constructor for Ellipse'''
self.__semi_major_axis = semi_major_axis
self.__semi_minor_axis = semi_minor_axis
super().__init__(name)
def get_semi_major_axis(self):
'''returns length of a rectangle object'''
return self.__semi_major_axis
def set_semi_major_axis(self, semi_major_axis):
'''set length of a rectangle'''
self.__semi_major_axis = semi_major_axis
def get_semi_minor_axis(self):
'''returns width of a rectangle object'''
return self.__semi_minor_axis
def set_semi_minor_axis(self, semi_minor_axis):
'''set width of a rectangle'''
self.__semi_minor_axis = semi_minor_axis
def get_perimeter(self):
'''Returns perimeter of an Ellipse.'''
sum_of_squares = (self.__semi_major_axis**2 + self.__semi_minor_axis**2)
perimeter = 2*self.PI*math.sqrt( sum_of_squares / 2)
return perimeter
def get_area(self):
'''Returns area of an Ellipse'''
return self.PI * self.__semi_major_axis * self.__semi_minor_axis
class Square(Rectangle):
'''Child class of a Rectangle class'''
def __init__(self, side):
super().__init__(side, side, name="Square")
def get_side(self):
return self.get_length()
def set_side(self, side):
self.set_length(side)
self.set_width(side)
class Circle(Ellipse):
'''Child class of a Ellipse'''
def __init__(self, radius):
super().__init__(radius, radius, name="Circle")
def get_radius(self):
return self.get_semi_major_axis()
def set_radius(self, radius):
self.set_semi_major_axis(radius)
self.set_semi_minor_axis(radius)
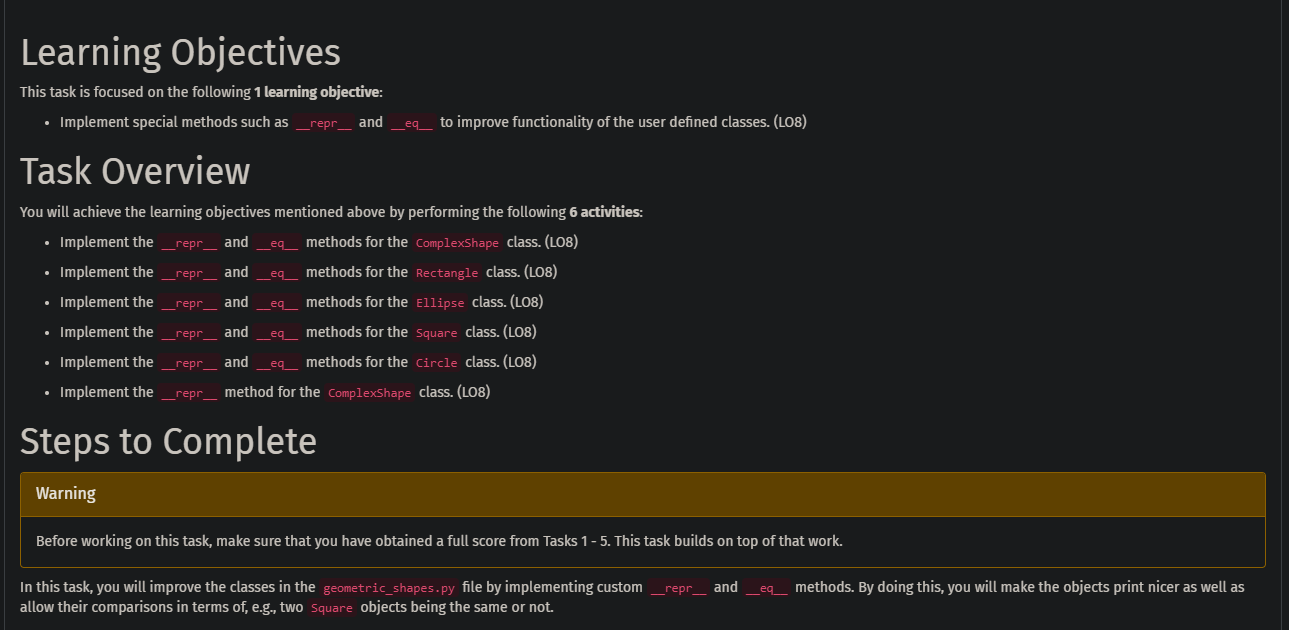
Learning Objectives This task is focused on the following 1 learning objective: - Implement special methods such as _ repr_ and _eq_ to improve functionality of the user defined classes. (LO8) Task Overview You will achieve the learning objectives mentioned above by performing the following 6 activities: - Implement the _repr_ and _ eq_ methods for the Complexshape class. (LO8) - Implement the _ repr__ and _eq_ methods for the Rectangle class. (LO8) - Implement the _repr_ and _eq_ methods for the Ellipse class. (LO8) - Implement the _repr_ and _eq_ methods for the square class. (LO8) - Implement the _repr_ and _ eq__ methods for the Circle class. (LO8) - Implement the _repr_ method for the Complexshape class. (LO8) Steps to Complete Warning Before working on this task, make sure that you have obtained a full score from Tasks 1 - 5 . This task builds on top of that work. allow their comparisons in terms of, e.g., two square objects being the same or not.
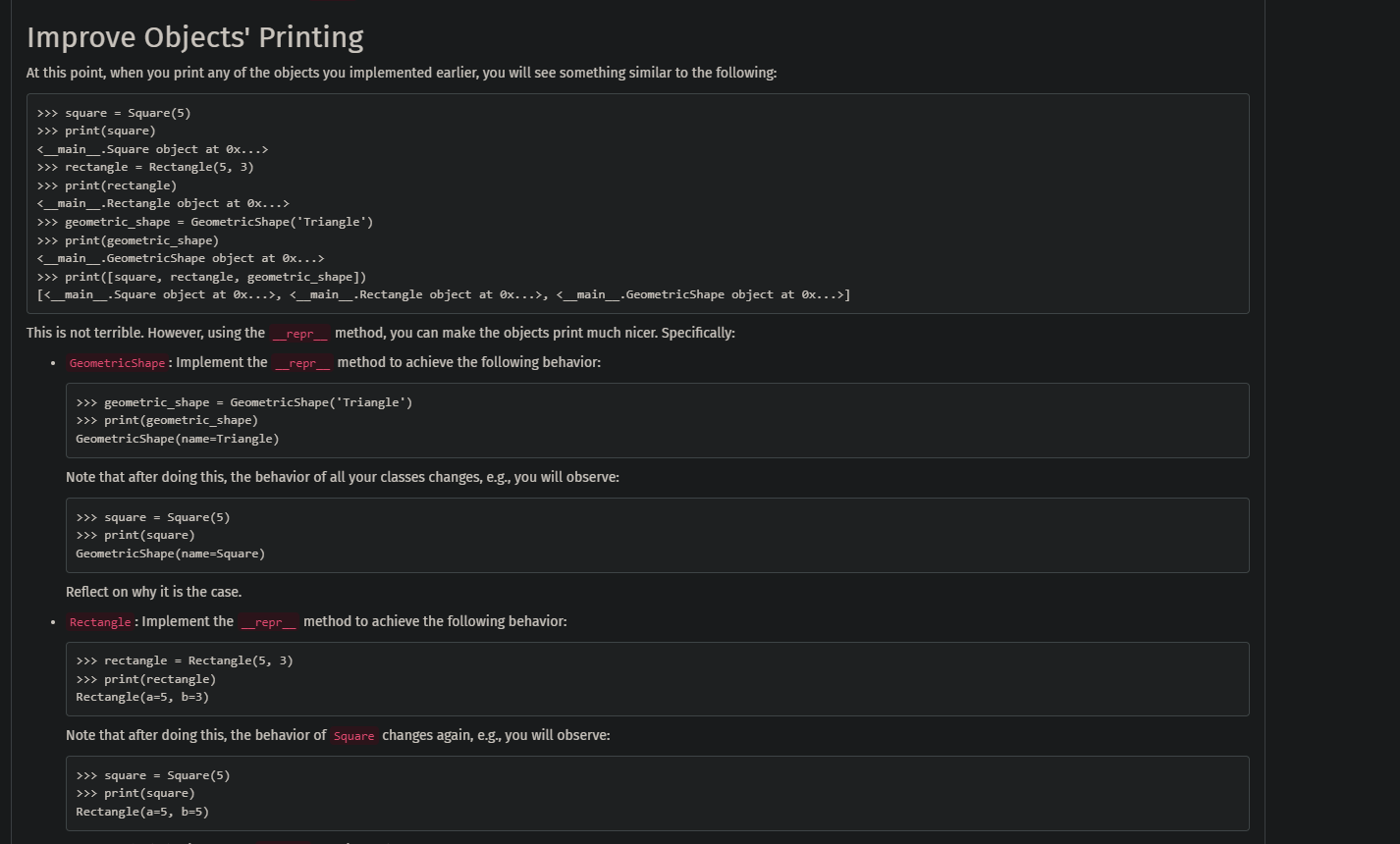
Improve Objects' Printing At this point, when you print any of the objects you implemented earlier, you will see something similar to the following: This is not terrible. However, using the __repr__ method, you can make the objects print much nicer. Specifically: - GeometricShape : Implement the _repr_ method to achieve the following behavior: >>> geometric_shape = GeometricShape('Triangle') >>> print(geometric_shape) GeometricShape(name=Triangle) Note that after doing this, the behavior of all your classes changes, e.g., you will observe: >>> square = Square(5) >>> print(square) GeometricShape(name=Square) Reflect on why it is the case. - Rectangle : Implement the _repr_ method to achieve the following behavior: >>> rectangle = Rectangle (5,3) >>> print(rectangle) Note that after doing this, the behavior of Square changes again, e.g., you will observe: Rectangle (a=5,b=5)
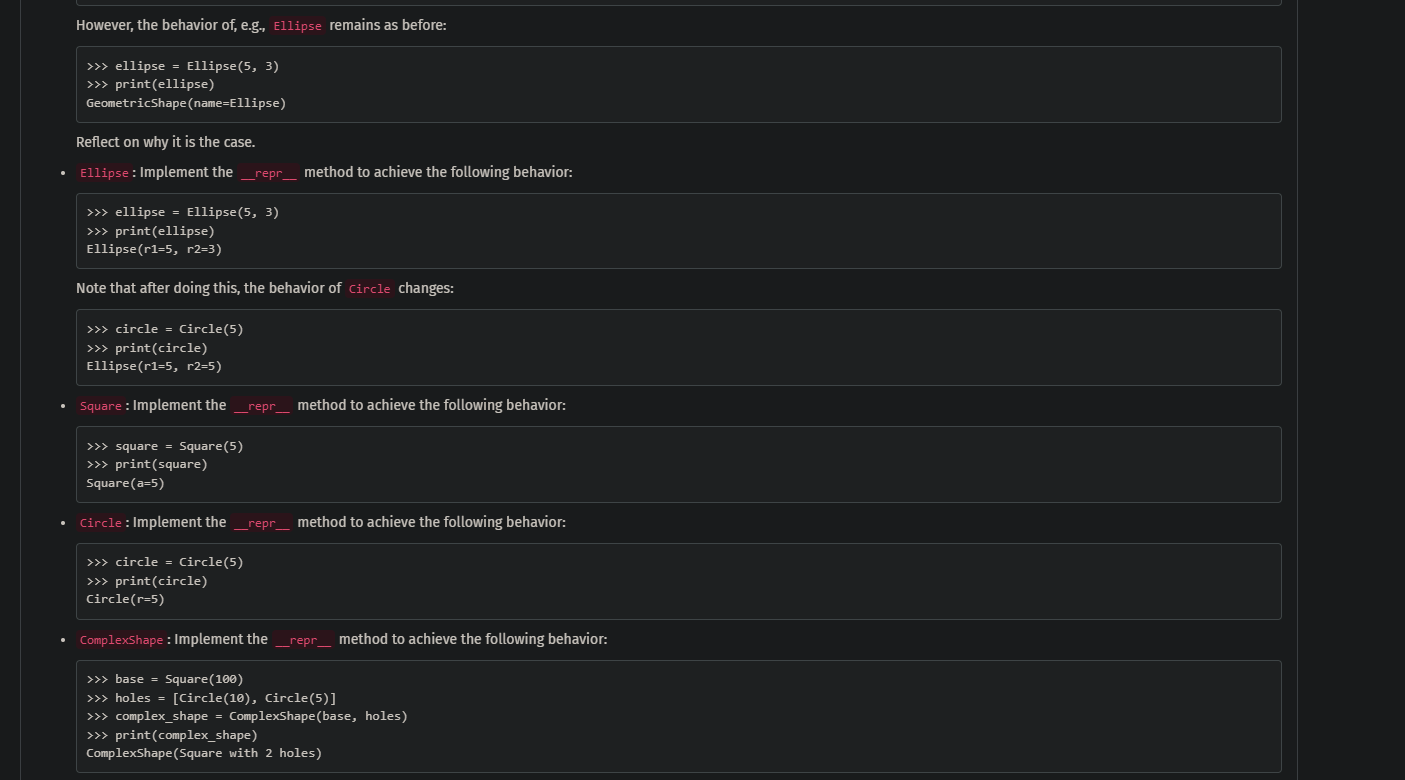
However, the behavior of, e.g., Ellipse remains as before: >>> ellipse = Ellipse (5,3) >> print(ellipse) GeometricShape(name=Ellipse) ? Reflect on why it is the case. - Ellipse: Implement the _repr__ method to achieve the following behavior: Ellipse(r1=5, r2=3) ? Note that after doing this, the behavior of circle changes: ?>> circle = Circle(5) >> print(circle) Ellipse(r1=5, r2=5) ? - Square: Implement the _repr__ method to achieve the following behavior: >>> square = Square(5) >>> print(square) Square (a=5)? - Circle: Implement the _repr__ method to achieve the following behavior: ?>> circle = Circle(5) >> print(circle) Circle (r=5)? - Complexshape: Implement the _repr_ method to achieve the following behavior:
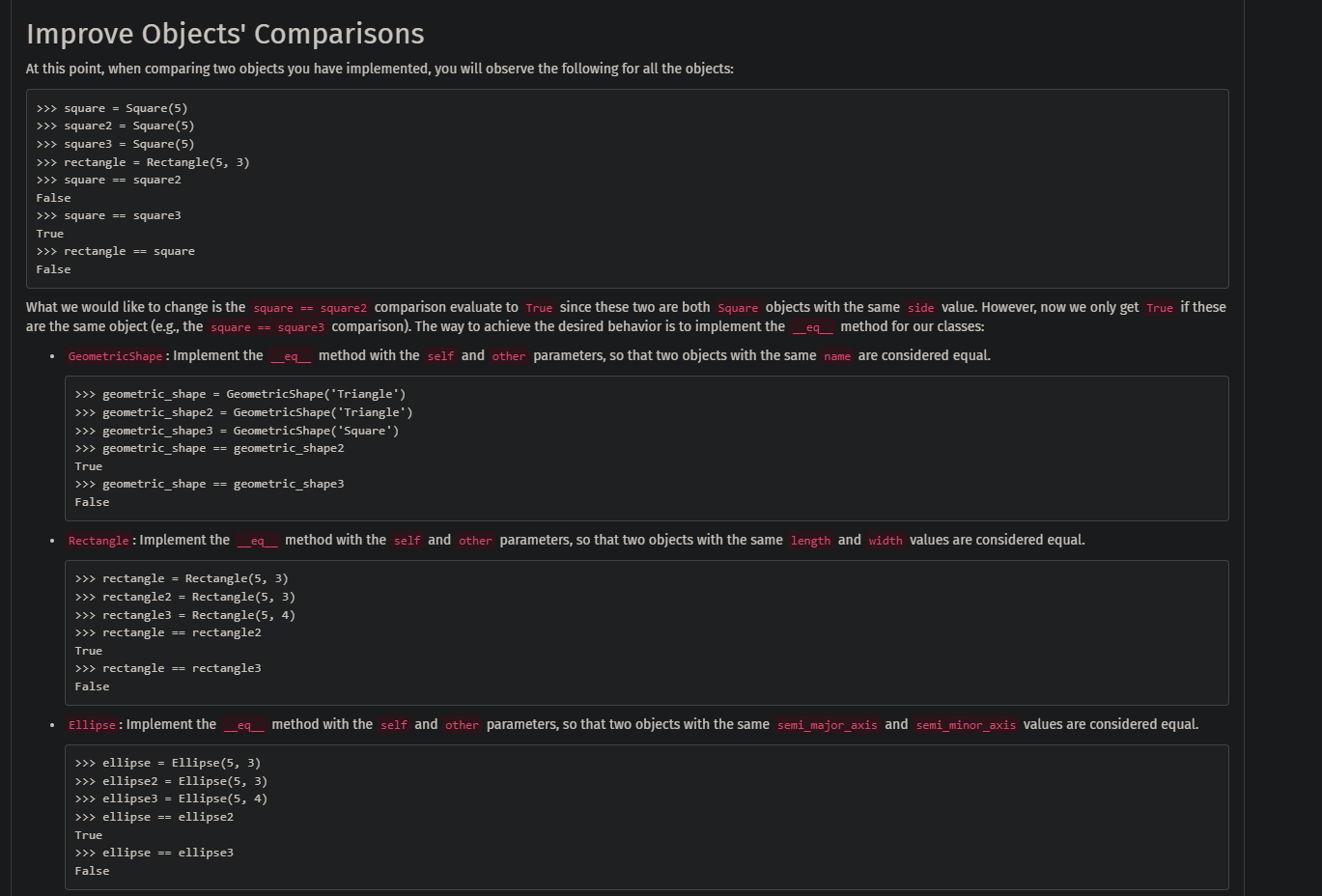
At this point, when comparing two objects you have implemented, you will observe the following for all the objects: >>> square = Square (5) >>> square 2= Square (5) >>> square 3= Square (5) >>> rectangle = Rectangle(5, 3) >>> square == square 2 False >>> square == square 3 True >>> rectangle = = square False are the same object (e.g., the square == square3 comparison). The way to achieve the desired behavior is to implement the _eq _ method for our classes: - GeometricShape: Implement the _eq__ method with the self and other parameters, so that two objects with the same name are considered equal. >>> geometric_shape = Geometric_Shape('Triangle') >>> geometric_shape2 = GeometricShape('Triangle') >>> geometric_shape 3= GeometricShape('Square') >>> geometric_shape == geometric_shape2 True >>> geometric_shape == geometric_shape3 False - Rectangle: Implement the _eq_ method with the self and other parameters, so that two objects with the same length and width values are considered equal. >>> rectangle =Rectangle(5,3) >>> rectangle 2=Rectangle(5,3) >>> rectangle 3=Rectangle(5,4) >>> rectangle = rectangle 2 True >>> rectangle = rectangle 3 False - Ellipse: Implement the _eq__ method with the self and other parameters, so that two objects with the same semi_major_axis and semi_minor_axis values are considered equal. >>> ellipse = Ellipse (5,3) >> ellipse2 = Ellipse (5,3) >>> ellipse3 = Ellipse (5,4) >> ellipse = e ellipse2 True >> ellipse = = ellipse3 False
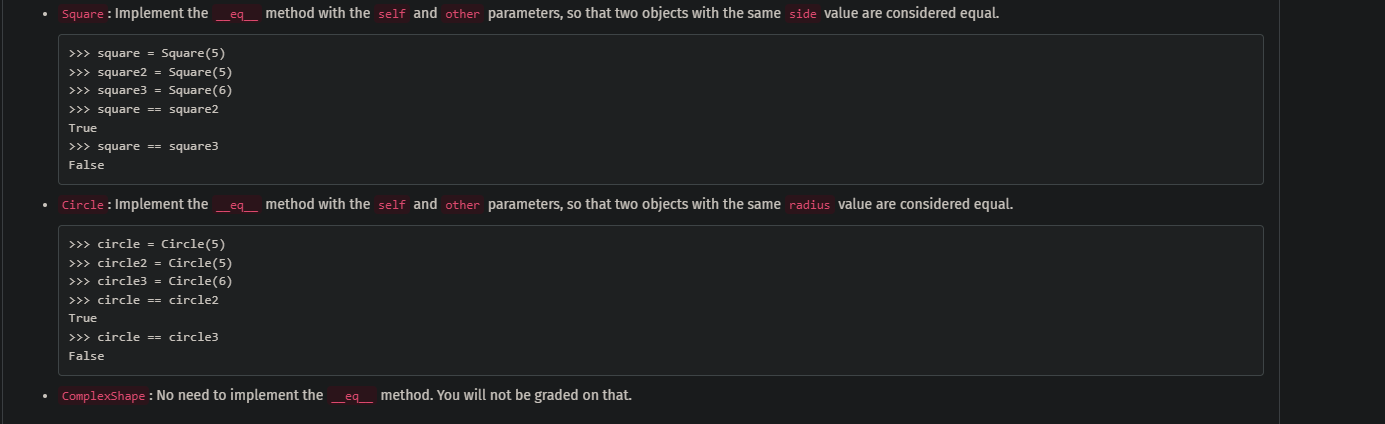
- Square: Implement the _eq__ method with the self and other parameters, so that two objects with the same side value are considered equal. >>> square = square (5) >>> square = square (5) >>> square 3= square (6) >>> square == square 2 True >>> square == square3 False - Circle: Implement the _eq_ method with the self and other parameters, so that two objects with the same radius value are considered equal. ?> circle = Circle (5) ?>> circle2 = Circle (5) ?>> circle3 = Circle (6) ?>> circle == circle True ?>> circle == circle3 False - Complexshape: No need to implement the _eq _ method. You will not be graded on that.




