Home /
Expert Answers /
Physics /
need-part-a-ch9-q7-learning-goal-to-practice-problem-solving-strategy-9-1-rotational-energy-a-stri-pa200
(Solved): NEED PART A ch9 q7 Learning Goal: To practice Problem-Solving Strategy 9.1 Rotational energy. A stri ...
NEED PART A
ch9 q7

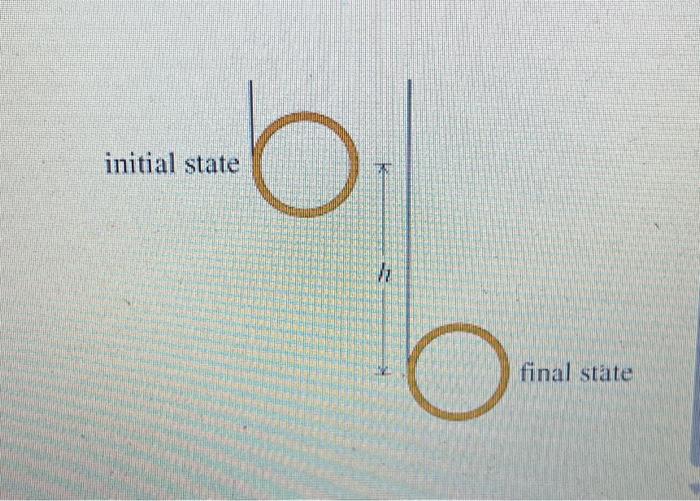





Learning Goal: To practice Problem-Solving Strategy 9.1 Rotational energy. A string is attached to the rim of a small hoop of radius and mass and then wrapped several times around the rim. If the free end of the string is held in place and the hoop is released from rest and allowed to drop. as shown in the figure ( Figure 1), calculate the angular speed and the translational speed of the rotating hoop after it has descended . Use for the acceleration due to gravity.
Problem-Solving Strategy 9.1 Rotational energy SET UP 1. Identify the system you will analyze, and decide on the initial and final states (positions and velocities) you will use in solving the problem. Draw one or more sketches showing the initial and final states. 2. Define your coordinate system, particularly the zero points for gravitational and elastic potential energies (the point at which in the case of gravitational potential energy or at which the spring is relaxed in the case of elastic potential energy). 3. List the initial and final kinetic and potential energies, that is, , and . Some of these will be known and some unknown. Use algebraic symbols for any unknown coordinates or velocities. Note that includes both gravitational and elastic potential energy, and includes both translational and rotational kinetic energy. Recall that for an object that rolls without slipping, the speed of the center of mass is given by SOLVE 4. Write expressions for the total initial mechanical energy and for the total final mechanical energy, equate them, and solve to find whatever unknown quantity is required REFLECT 5. Take a hard look at your results to see whether they make sense. Are they within the general range of magnitudes you expected? If you change one of the given quantities, do the results change in a way you can predict?
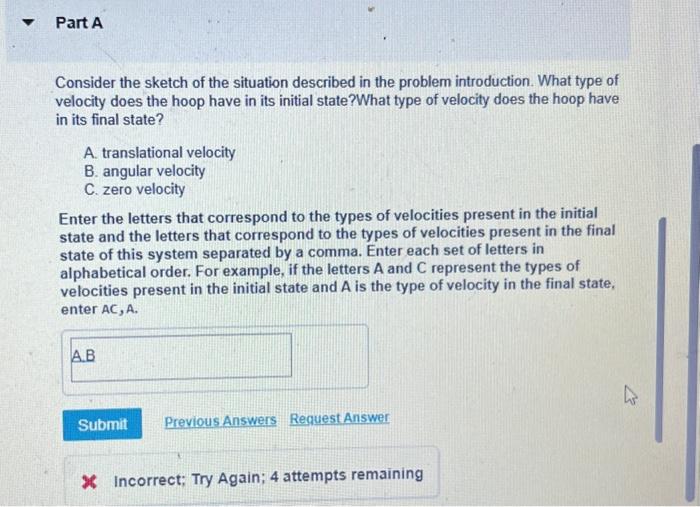
Consider the sketch of the situation described in the problem introduction. What type of velocity does the hoop have in its initial state?What type of velocity does the hoop have in its final state? A. translational velocity B. angular velocity C. zero velocity Enter the letters that correspond to the types of velocities present in the initial state and the letters that correspond to the types of velocities present in the final state of this system separated by a comma. Enter each set of letters in alphabetical order. For example, if the letters and represent the types of velocities present in the initial state and is the type of velocity in the final state, enter . 16 Incorrect; Try Again; 4 attempts remaining
Expert Answer
In the initial state, the hoop has zero velocity.