(Solved): python programming ( this is a big question with multiple little parts) 1- Define two numpy arrays a ...
python programming ( this is a big question with multiple little parts)
1-
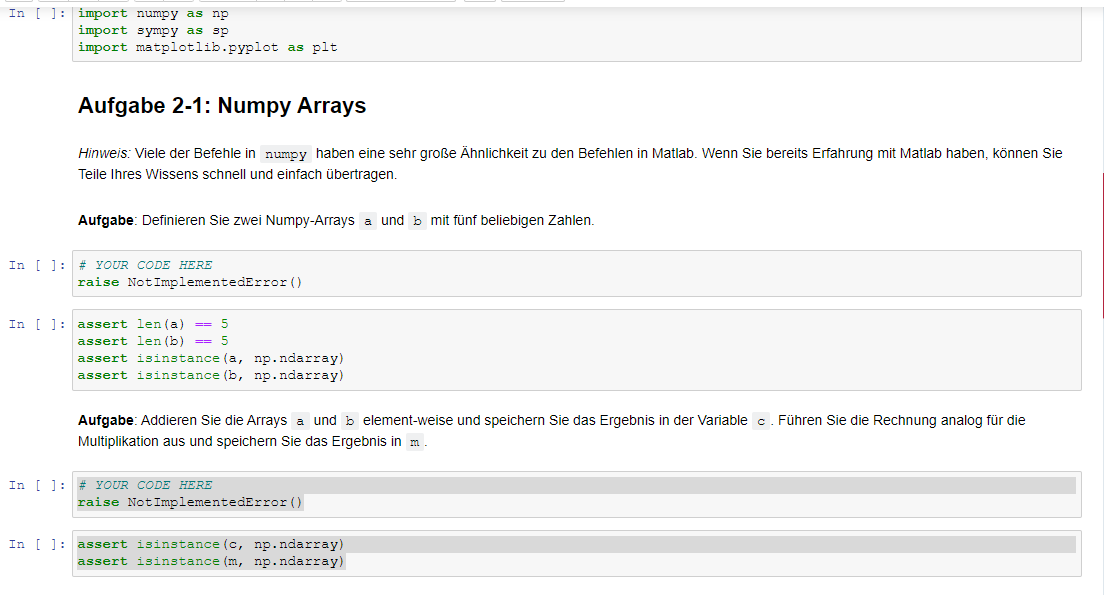
Define two numpy arrays a and b with five arbitrary numbers.
# YOUR CODE HERE
raise NotImplementedError()
assert len(a) == 5
assert len(b) == 5
assert isinstance(a, np.ndarray)
assert isinstance(b, np.ndarray)
2-
Add the arrays a and b element by element and store the result in the variable c. Perform the calculation analogously for the multiplication and store the result in m.
# YOUR CODE HERE
raise NotImplementedError()
assert isinstance(c, np.ndarray)
assert isinstance(m, np.ndarray)
3-
Multidimensional arrays
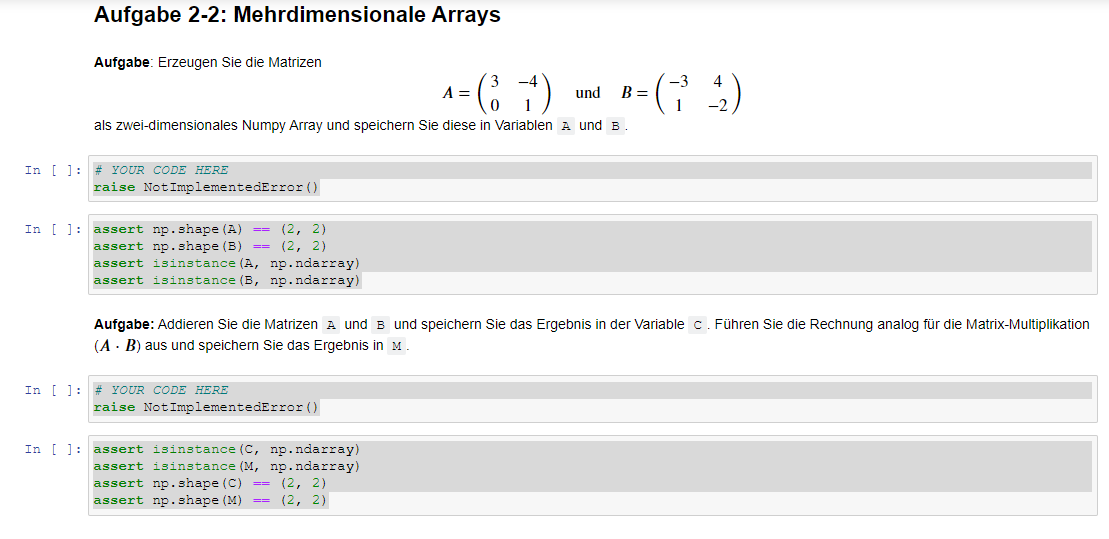
Create the matrices:A&B ( you find them in the picture under Aufgabe 2-2)
als zwei-dimensionales Numpy Array und speichern Sie diese in Variablen A und B
# YOUR CODE HERE
raise NotImplementedError()
assert np.shape(A) == (2, 2)
assert np.shape(B) == (2, 2)
assert isinstance(A, np.ndarray)
assert isinstance(B, np.ndarray)
4-
Add the matrices A and B and store the result in the variable C. Perform the calculation analogously for the matrix multiplication ( ????????? ) and store the result in M.
# YOUR CODE HERE
raise NotImplementedError()
assert isinstance(C, np.ndarray)
assert isinstance(M, np.ndarray)
assert np.shape(C) == (2, 2)
assert np.shape(M) == (2, 2)
5-
Eigenvalue decomposition
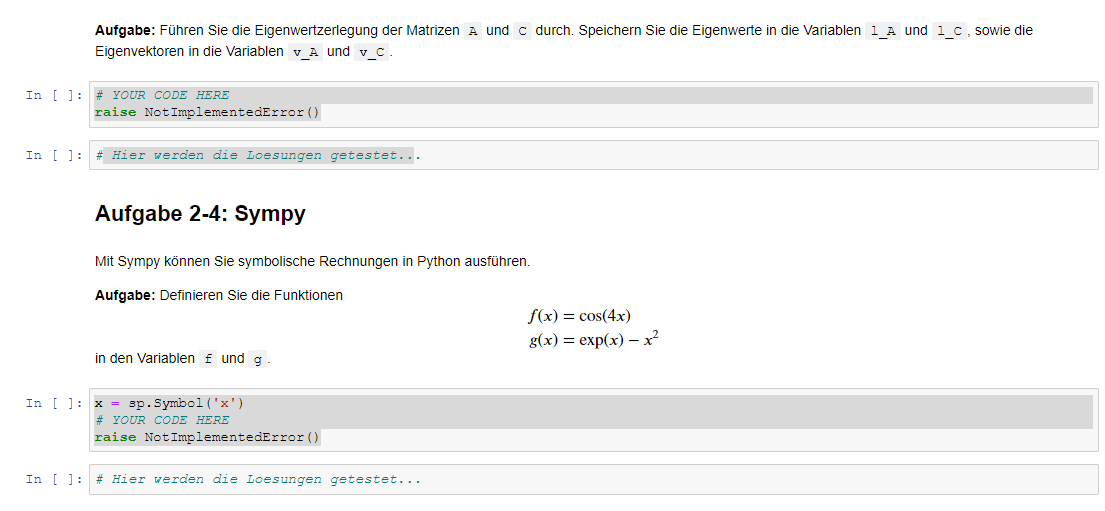
Perform the eigenvalue decomposition of the matrices A and C. Store the eigenvalues in the variables l_A and l_C, and the eigenvectors in the variables v_A and v_C.
# YOUR CODE HERE
raise NotImplementedError()
# Here the solutions are tested.
6-
Sympy :Sympy lets you perform symbolic computations in Python. Define the functions:
????(????)=cos(4????)
????(????)=exp(????)?????^2 , in the variables f and g.
x = sp.Symbol('x')
# YOUR CODE HERE
raise NotImplementedError()
# Here the solutions are tested.
7-
Calculate the root functions of f using integration of Sympy and store them in F.
# YOUR CODE HERE
raise NotImplementedError()
# Here the solutions are tested.
8-
Calculate the definite integral
????=?????(????)d???? ( from -5 to 6 )
and store the solution in the variable G..
# YOUR CODE HERE
raise NotImplementedError()
# Here the solutions are tested.
9-
Matplotlib
Plot the points (????????,????????) , where ???????? and ???????? are the elements from
the arrays a and b, respectively.
On the one hand, the points themselves should be marked, and on the
other hand, they should also be connected.
Give the x-axis the label "values from a" and the y-axis the label
"values from b".
# YOUR CODE HERE
raise NotImplementedError()
Expert Answer
-> CODE import numpy as np import sympy as sp import matplotlib.pyplot as plt # PART-1 a = np.array([1,2,3,4,5]) b = np.array([1.1,2.2,3.3,4.4,5.5]) assert len(a)==5 assert len(b)==5 assert isinstanc
![Aufgabe: Berechnen Sie die Stammfunktionen von mittels Integration von Sympy und speichern Sie diese in F.
In [ ] # YOUR CODE](https://media.cheggcdn.com/media/124/124657b9-6a40-4d25-b645-9360a0644f0a/phpho7m0W)