Home /
Expert Answers /
Advanced Physics /
question-2-a-two-stage-common-source-amplifier-consisting-of-two-n-channel-mosfets-m-i-and-m-2-pa810
(Solved): Question 2 A two-stage common source amplifier consisting of two n-channel MOSFETs, M_(I) and M_(2), ...
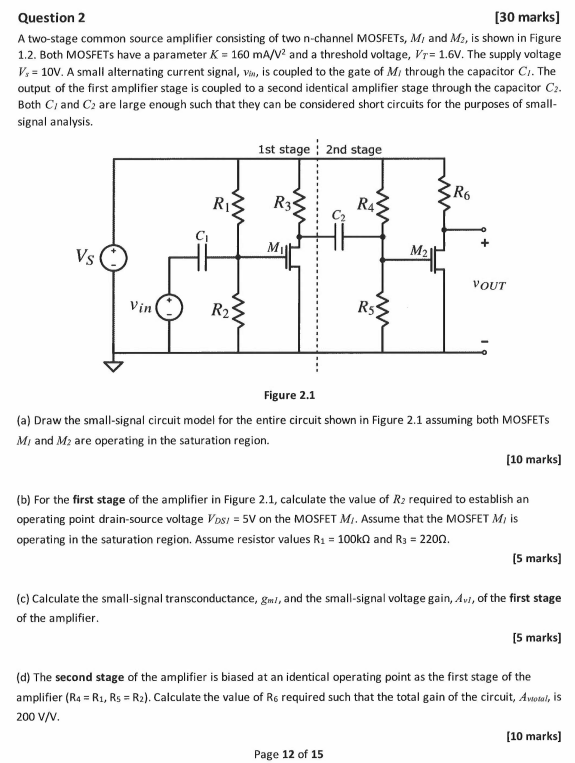
Question 2
A two-stage common source amplifier consisting of two n-channel MOSFETs, M_(I) and M_(2), is shown in Figure 1.2. Both MOSFETs have a parameter K=160(mA)/(V^(2)) and a threshold voltage, V_(T)=1.6V. The supply voltage V_(s)=10V. A small alternating current signal, v_(in), is coupled to the gate of M_(i) through the capacitor C_(l). The
output of the first amplifier stage is coupled to a second identical amplifier stage through the capacitor C_(2).Both C_(1) and C_(2) are large enough such that they can be considered short circuits for the purposes of small-signal analysis.
Figure 2.1
(a) Draw the small-signal circuit model for the entire circuit shown in Figure 2.1 assuming both MOSFETs M_(1) and M_(2) are operating in the saturation region.
[10 marks]
(b) For the first stage of the amplifier in Figure 2.1, calculate the value of R_(2) required to establish an operating point drain-source voltage V_(DSI)=5V on the MOSFET M_(i). Assume that the MOSFET M_(i) is operating in the saturation region. Assume resistor values R_(1)=100k\Omega and R_(3)=220\Omega .
[5 marks]
(c) Calculate the small-signal transconductance, g_(mI), and the small-signal voltage gain, A_(vl)R_(4)=R_(1),R_(5)=R_(2) R_(6) required such that the total gain of the circuit, A_(wotal, ), is
200(V)/(V).
(d) The second stage of the amplifier is biased at an identical operating point as the first stage of the amplifier (R4 = R1, R5 = R2). Calculate the value of R6 required such that the total gain of the circuit A_(vtotal), is 200 (V)/(V).