Home /
Expert Answers /
Chemical Engineering /
the-activity-values-of-a-in-a-b-solution-at-1000-k-depending-on-the-composition-are-presented-pa696
(Solved): The activity values of A in A-B solution at 1000 K depending on the composition are presented ...
The activity values ??of A in A-B solution at 1000 K depending on the composition are presented in the table below. Calculate the activity of B in solution XB = 0.45 at 1000 K.
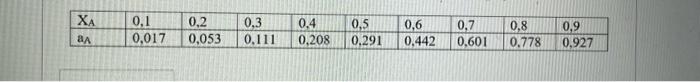
\begin{tabular}{|l|l|l|l|l|l|l|l|l|l|} \hline & 0,1 & 0,2 & 0,3 & 0,4 & 0,5 & 0,6 & 0,7 & 0,8 & 0,9 \\ \hline & 0,017 & 0,053 & 0,111 & 0,208 & 0,291 & 0,442 & 0,601 & 0,778 & 0,927 \\ \hline \end{tabular}
Expert Answer
To calculate the activity of B in the solution, we can use the relation: ?B = XB * ?B* ---- (1) where ?B is the activity coefficient of B, XB is the mole fraction of B in the solution, and ?B* is the standard state activity coefficient of B. However, we don’t have the values of ?B* for this problem. So, we will assume that ?B* is equal to unity (i.e., ideal solution). In this case, we can simplify Equation (1) as: ?B = XB Now, we need to find the activity of A in the solution for XB = 0.45 using the given data. We can use the relation: Ln ?A = -ln(XA) + XA * (1 – XA) * ?A Where ?A is the excess Gibbs energy of mixing for A-B solution, which can be calculated using the data given in the table as: ?A = RT * ln(aA/XA) ---- (2) Where R is the gas constant and T is the temperature in Kelvin. Please refer to the solution for this step